Ephemeral Environments Automation: Powering Agile Innovation Through Short-Lived Environments
Imagine a theatre troupe rehearsing a complex play. Every time they want to test a new scene, a full stage setup—with lights, props, and backdrops—appears instantly, tailored to that scene. Once rehearsed, it vanishes without a trace, leaving no clutter behind.
That’s the essence of ephemeral environments in DevOps—temporary, self-contained replicas of production systems created for testing new features safely and efficiently.
Ephemeral environments enable teams to move faster, collaborate better, and eliminate the long-standing friction between development, testing, and deployment cycles.
The Need for Speed in Modern Development
In traditional workflows, developers often wait for a shared staging environment to test their code. This delay not only slows down delivery but also increases the risk of conflicts when multiple teams use the same environment simultaneously.
Ephemeral environments flip this model on its head. Each feature branch or pull request gets its own isolated environment—complete with databases, APIs, and dependencies—mirroring production precisely. When the testing is done or the branch is merged, the environment automatically shuts down.
For professionals seeking to master this agility, structured programs such as a DevOps training in Chennai provide hands-on experience with cloud-based automation tools that make ephemeral setups both reliable and scalable.
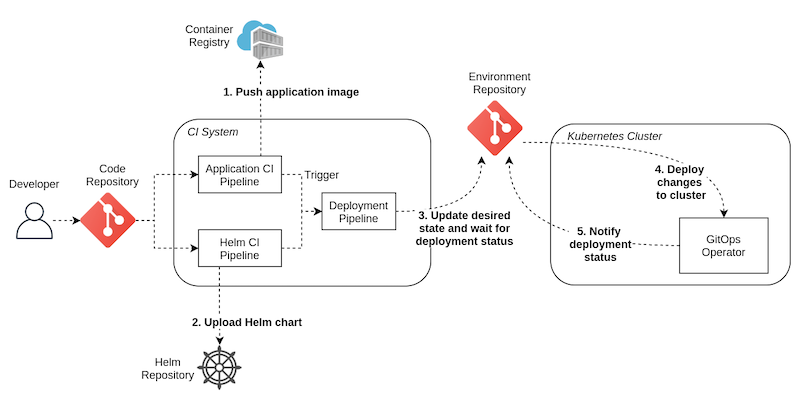
How Ephemeral Environments Work
At the heart of this system lies automation. Tools like Kubernetes, Terraform, and Docker Compose are often orchestrated through CI/CD pipelines. When a developer opens a pull request, automation scripts trigger the following sequence:
- Provisioning: Infrastructure is dynamically created using Infrastructure as Code (IaC).
- Configuration: Services, databases, and dependencies are configured to match production.
- Testing: The feature runs through automated and manual testing within this environment.
- Teardown: Once testing completes or the branch merges, resources are destroyed to save cost.
This process reduces infrastructure waste, minimises manual intervention, and ensures consistent testing environments across all development stages.
Advantages of Ephemeral Environments
Ephemeral environments deliver several key benefits that traditional setups can’t match:
- Rapid Feedback Loops: Developers get immediate feedback on their changes without waiting for shared resources.
- High Fidelity Testing: Since each environment replicates production, testing accuracy improves dramatically.
- Cost Efficiency: Because environments exist only temporarily, cloud usage costs drop significantly.
- Improved Collaboration: Testers, product managers, and stakeholders can review isolated features in real time.
By empowering teams to test, validate, and iterate faster, ephemeral environments are becoming the cornerstone of modern DevOps culture.
Challenges in Implementation
Despite their advantages, ephemeral environments come with hurdles.
Automation must be flawless—one misconfigured script can spin up broken environments or consume excessive resources.
Secrets management also poses challenges; temporary environments must access sensitive credentials securely without leaving traces behind.
Scalability is another concern. Large enterprises running dozens of parallel branches may face resource bottlenecks or governance issues.
Addressing these requires robust monitoring and careful orchestration strategies—skills often refined through expert-led sessions in a DevOps training in Chennai, where learners gain practical insight into environment lifecycle management.
The Future: Seamless DevOps Ecosystems
As DevOps continues to evolve, ephemeral environments represent the next logical step in continuous integration and continuous delivery. In the near future, AI-driven pipelines may automatically predict the ideal configurations for each environment, optimise resource allocation, and detect anomalies before they impact development.
The goal isn’t just automation—it’s intelligent automation that adapts in real time to project needs. When done right, ephemeral environments bridge the gap between innovation and reliability, ensuring that every code change reaches production faster, safer, and smarter.
Conclusion
Ephemeral environments redefine agility in software development. They transform infrastructure from a bottleneck into a dynamic enabler of innovation.
By giving each idea its own short-lived, high-fidelity space to prove itself, DevOps teams can experiment fearlessly and deploy confidently.
For professionals eager to build such resilient and efficient pipelines, mastering the principles of ephemeral automation through a solid DevOps foundation is essential. With the right mindset and skills, the journey from idea to deployment becomes as seamless as a stage rehearsal that always ends in a flawless performance.